| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Sextans |
| Right ascension | 10h 07m 56.29556s[1] |
| Declination | −0° 22′ 17.8621″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.49[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A0 III[3] |
| U−B color index | −0.07[2] |
| B−V color index | −0.04[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 10.00[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −25.83[1] mas/yr Dec.: −4.25[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 11.51 ± 0.98 mas[1] |
| Distance | 280 ± 20 ly (87 ± 7 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.29±0.21[5] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 2.57±0.32[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 3.07[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 90[6] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.55[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 9,984[8] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.03±0.18[7] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 21[9] km/s |
| Age | 385[6] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
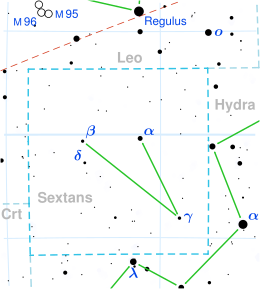
Alpha Sextantis (α Sex, α Sextantis) is the brightest star in the equatorial constellation of Sextans.[11] It is visible to the naked eye on a dark night with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.49.[2] The distance to this star, as determined from parallax measurements,[1] is around 280 light years. This is considered an informal "equator star", as it lies less than a quarter of a degree south of the celestial equator. In 1900, it was 7 minutes of arc north of the equator. As a result of a shift in the Earth's axial tilt, it crossed over to the southern hemisphere in December 1923.[12]
The variability of Alpha Sextantis was discovered by Aven Magded Hamadamen and included in the International Variable Star Index.[13] The star undergoes pulsations with a period of 9.1 hours.[6]
This is an evolved A-type giant star with a stellar classification of A0 III.[3] It has around 2.5[6] times the mass of the Sun and three[6] times the Sun's radius. The abundance of elements is similar to that in the Sun.[7] It radiates 90 times the solar luminosity[6] from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 9,984 K.[8] Alpha Sextantis is nearing the end of its life as a main-sequence star; it is around 385[6] million years old with a projected rotational velocity of 21 km/s.[9]
- ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
vanLeeuwen2007was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
Mermilliod1986was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Cowley1969was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Gontcharov2006was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Gerbaldi1999was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h i Cite error: The named reference
Bowmanwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
Pintado2003was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Mcdonald2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Royer2002was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
SIMBADwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Darlingwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Kalerwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "VSX : Detail for alf Sex". www.aavso.org. Retrieved 2023-12-02.