This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
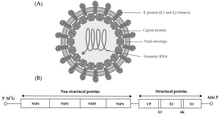
Alphavirus is a genus of RNA viruses, the sole genus in the Togaviridae family. Alphaviruses belong to group IV of the Baltimore classification of viruses, with a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome.[1] There are 32 alphavirus species, which infect various vertebrates such as humans, rodents, fish, birds, and larger mammals such as horses, as well as invertebrates.[1] Alphaviruses that can infect both vertebrates and arthropods are referred dual-host alphaviruses, while insect-specific alphaviruses such as Eilat virus and Yada yada virus are restricted to their competent arthropod vector.[2] Transmission between species and their vertebrate hosts (including human) occurs mainly via mosquitoes, making the alphaviruses a member of the collection of arboviruses – or arthropod-borne viruses.[1] Alphavirus particles are enveloped, have a 70 nm diameter, tend to be spherical (although slightly pleomorphic), and have a 40 nm isometric nucleocapsid.[3]
- ^ a b c Ahola, Tero; McInerney, Gerald; Merits, Andres (1 January 2021), Kielian, Margaret; Mettenleiter, Thomas C.; Roossinck, Marilyn J. (eds.), "Chapter Four - Alphavirus RNA replication in vertebrate cells", Advances in Virus Research, vol. 111, Academic Press, pp. 111–156, doi:10.1016/bs.aivir.2021.07.003, retrieved 20 August 2024
- ^ Elrefaey AM, Abdelnabi R, Rosales Rosas AL, Wang L, Basu S, Delang L (31 August 2020). "Understanding the Mechanisms Underlying Host Restriction of Insect-Specific Viruses". Viruses. 12 (9): 964. doi:10.3390/v12090964. PMC 7552076. PMID 32878245.
- ^ Chen R, Mukhopadhyay S, Merits A, Bolling B, Nasar F, Coffey LL, et al. (June 2018). "ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Togaviridae". The Journal of General Virology. 99 (6): 761–2. doi:10.1099/jgv.0.001072. PMID 29745869.