
| |
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate
| |
| Other names
Monoammonium phosphate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.877 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E342(i) (antioxidants, ...) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H6NO4P | |
| Molar mass | 115.025 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white crystals |
| Odor | none |
| Density | 1.80 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 190 °C (374 °F; 463 K) |
| (g/dL) 28 (10 °C) 36 (20 °C) 44 (30 °C) 56 (40 °C) 66 (50 °C) 81 (60 °C) 99 (70 °C) 118 (80 °C) 173 (100 °C) [2][3] | |
| Solubility | insoluble in ethanol[2] insoluble in acetone |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.525 |
| Structure | |
| tetragonal | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−1445.07 kJ/mol[4] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H319 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
5750 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Ammonium phosphate Diammonium phosphate |
Other cations
|
Monosodium phosphate Potassium dihydrogen phosphate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
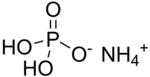
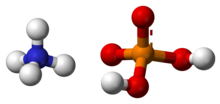
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP), also known as monoammonium phosphate (MAP)[5] is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)(H2PO4). ADP is a major ingredient of agricultural fertilizers[6] and dry chemical fire extinguishers. It also has significant uses in optics[7] and electronics.[8]
- ^ Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. 4–40. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
DXuwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Chemical Book: "Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate". Accessed on 2018-08-14.
- ^ National Bureau of Standards. Selected Values of Chemical Thermodynamic Properties. Technical note 270-3. 1968 [1]
- ^ "Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP)" (PDF). www.mosaicco.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 5 June 2015.
- ^ IPNI. "Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP)" (PDF). www.ipni.net. International Plant Nutrition Institute. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Amnon Yariv, Pochi Yeh (1984). Optical Waves in Crystals. Wiley, Inc.
- ^ Willem Hackmann (1984). Seek and Strike: Sonar, Anti-Submarine Warfare and the Royal Navy, 1914–1954. Her Majesty's Stationery Office. ISBN 0-11-290423-8.
