| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ammonium nitrate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.680 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 0222 – with > 0.2% combustible substances 1942 – with ≤ 0.2% combustible substances 2067 – fertilizers 2426 – liquid |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NH4NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 80.043 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.725 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 169.6 °C (337.3 °F; 442.8 K) |
| Boiling point | approx. 210 °C (410 °F; 483 K) decomposes |
| Endothermic 118 g/100 ml (0 °C) 150 g/100 ml (10 °C) 192 g/100 ml (20 °C) 297 g/100 ml (40 °C) 410 g/100 ml (60 °C) 576 g/100 ml (80 °C) 1024 g/100 ml (100 °C)[1] | |
| −33.6×10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| orthorhombic[2] | |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | very low |
| Friction sensitivity | very low |
| Detonation velocity | 2500 m/s |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Explosive, Oxidizer |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H201, H271, H319 | |
| P220, P221, P264, P271, P280, P372 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
2085–5300 mg/kg (oral in rats, mice)[3] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Ammonium nitrite |
Other cations
|
Sodium nitrate Potassium nitrate Hydroxylammonium nitrate |
Related compounds
|
Ammonium perchlorate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
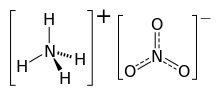
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula NH4NO3. It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, although it does not form hydrates. It is predominantly used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer.[5]
Its other major use is as a component of explosive mixtures used in mining, quarrying, and civil construction. It is the major constituent of ANFO, a popular industrial explosive which accounts for 80% of explosives used in North America; similar formulations have been used in improvised explosive devices.
Many countries are phasing out its use in consumer applications due to concerns over its potential for misuse.[6] Accidental ammonium nitrate explosions have killed thousands of people since the early 20th century.[6][7] Global production was estimated at 21.6 million tonnes in 2017.[8] By 2021, global production of ammonium nitrate was down to 16.7 million tonnes.[7]
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8
- ^ Kaniewski, Maciej; Huculak-Mączka, Marta; Zieliński, Jakub; Biegun, Marcin; Hoffmann, Krystyna; Hoffmann, Józef (2021). "Crystalline Phase Transitions and Reactivity of Ammonium Nitrate in Systems Containing Selected Carbonate Salts". Crystals. 11 (10): 1250. doi:10.3390/cryst11101250. ISSN 2073-4352.
- ^ Martel, B.; Cassidy, K. (2004). Chemical Risk Analysis: A Practical Handbook. Butterworth–Heinemann. p. 362. ISBN 1-903996-65-1.
- ^ "Hazard Rating Information for NFPA Fire Diamonds". Archived from the original on 17 February 2015. Retrieved 13 March 2015.
- ^ Zapp, Karl-Heinz (2012). "Ammonium Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_243. ISBN 9783527303854.
- ^ a b Ammonium nitrate sold by ton as U.S. regulation is stymied. Archived 28 February 2018 at the Wayback Machine – The Dallas Morning News
- ^ a b "Ammonium nitrate production by country, 2023 - knoema.com". Knoema.
- ^ "Ammonium nitrate production by country, 2019". Knoema. Retrieved 14 August 2020.
