| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Diammonium molybdate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.741 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
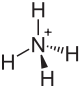
| (NH4)2MoO4 | |
| Molar mass | 196.02 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless monoclinic crystals |
| Density | 2.276 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | decomposes upon heating |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | insoluble in alcohol and liquid ammonia |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
1870 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 2200 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) 1600 mg/kg (cat, oral)[1] |
LDLo (lowest published)
|
120 mg Mo/kg (rat, oral) 120 mg Mo/kg (guinea pig, oral)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ammonium orthomolybdate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2MoO4. It is a white solid that is prepared by treating molybdenum trioxide with aqueous ammonia. Upon heating these solutions, ammonia is lost, to give ammonium heptamolybdate ((NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O).
- ^ a b "Molybdenum (soluble compounds, as Mo)". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).