| Angular frequency | |
|---|---|
 | |
Other names | angular speed, angular rate |
Common symbols | ω |
| SI unit | radian per second (rad/s) |
Other units | degrees per second (°/s) |
| In SI base units | s−1 |
Derivations from other quantities | ω=2π rad ⋅ ν, ω=dθ/dt |
| Dimension | |

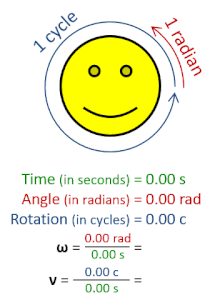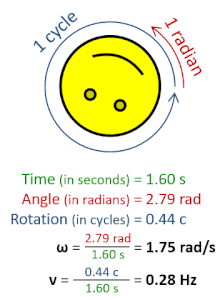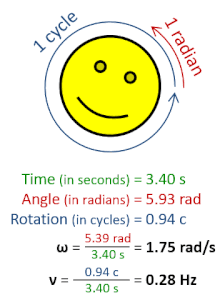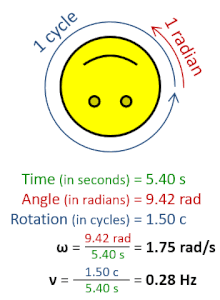
In physics, angular frequency (symbol ω), also called angular speed and angular rate, is a scalar measure of the angle rate (the angle per unit time) or the temporal rate of change of the phase argument of a sinusoidal waveform or sine function (for example, in oscillations and waves). Angular frequency (or angular speed) is the magnitude of the pseudovector quantity angular velocity.[1]
Angular frequency can be obtained multiplying rotational frequency, ν (or ordinary frequency, f) by a full turn (2π radians): ω = 2π rad⋅ν. It can also be formulated as ω = dθ/dt, the instantaneous rate of change of the angular displacement, θ, with respect to time, t.[2][3]
- ^ Cummings, Karen; Halliday, David (2007). Understanding physics. New Delhi: John Wiley & Sons, authorized reprint to Wiley – India. pp. 449, 484, 485, 487. ISBN 978-81-265-0882-2.(UP1)
- ^ "ISO 80000-3:2019 Quantities and units — Part 3: Space and time" (2 ed.). International Organization for Standardization. 2019. Retrieved 2019-10-23. [1] (11 pages)
- ^
Holzner, Steven (2006). Physics for Dummies. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley Publishing. pp. 201. ISBN 978-0-7645-5433-9.
angular frequency.
