| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
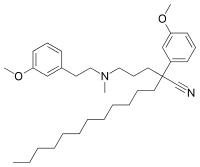
| IUPAC name
2-(3-methoxyphenyl)-2-[3-[2-(3-methoxyphenyl)ethyl-methylamino]propyl]tetradecanenitrile
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.072.899 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Anipamil |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C34H52N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 520.802 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Anipamil is a calcium channel blocker,[1] specifically of the phenylalkylamine type. This type is separate from its more common cousin Dihydropyridine. Anipamil is an analog of the more common drug verapamil, which is the most common type of phenylalkylamine style calcium channel blocker. Anipamil has been shown to be a more effective antiarrhythmic medication[2] than verapamil because it does not cause hypertension as seen in verapamil.[3] It is able to do this by bonding to the myocardium tighter than verapamil.[2]
- ^ Raddino, Riccardo; Poli, Enzo; Pasini, Evasio; Ferrari, Roberto (1992-09-01). "Effects of the novel calcium channel blocker, anipamil, on the isolated rabbit heart". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 346 (3): 339–344. doi:10.1007/BF00173549. ISSN 0028-1298. PMID 1383837. S2CID 20915840.
- ^ a b Pugsley, M.K. (1995-08-11). "Effects of anipamil, a long acting analog of verapamil, in pigs subjected to myocardial ischemia". Life Sciences. 57 (12): 1219–1231. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(95)02070-Y. PMID 7674811.
- ^ Lefrandt, J. D.; Heitmann, J.; Sevre, K.; Castellano, M.; Hausberg, M.; Fallon, M.; Fluckiger, L.; Urbigkeit, A.; Rostrup, M. (2001-11-01). "The effects of dihydropyridine and phenylalkylamine calcium antagonist classes on autonomic function in hypertension: the VAMPHYRE study". American Journal of Hypertension. 14 (11 Pt 1): 1083–1089. doi:10.1016/S0895-7061(01)02218-X. ISSN 0895-7061. PMID 11724204.