This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2015) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
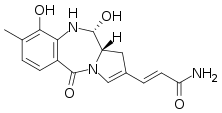
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E)-3-[(11S,11aS)-9,11-Dihydroxy-8-methyl-5-oxo-5,10,11,11a-tetrahydro-1H-pyrrolo[2,1-c] [1,4]benzodiazepin-2-yl]prop-2-enamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H17N3O4 | |
| Molar mass | 315.329 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Anthramycin is a pyrrolobenzodiazepine antibiotic with antitumor activity.[1] First derived from the thermophilic actinomycete Streptomyces refuineus by M. D. Tendler and S Korman in the 1950s, it was first successfully synthesized in a laboratory setting by Leimgruber et al. in 1965. Due to the unstable nature of the chemical structure, characterization of the species was done on its epimer, anthrmycin-11-methyl-ether. This derivative can be formed by recrystallization of anthramycin from hot methanol.
- ^ Kitamura, Tsuyoshi; Yoshihiro Sato; Miwako Mori (2004). "Synthetic study of (+)-anthramycin using ring-closing enyne metathesis and cross-metathesis". Tetrahedron. 60 (43): 9649–57. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2004.07.040.