| |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Anthracene-9,10-dione[2] | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 390030 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.408 |
| 102870 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3143 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 208.216 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow solid |
| Density | 1.438 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 284.8 °C (544.6 °F; 558.0 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 377 °C (711 °F; 650 K)[1] |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
possible carcinogen |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H350 | |
| P201, P202, P281, P308+P313, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 185 °C (365 °F; 458 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
quinone, anthracene |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
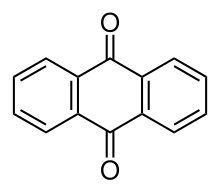
Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene, is an aromatic organic compound with formula C
14H
8O
2. Several isomers exist but these terms usually refer to 9,10-anthraquinone (IUPAC: 9,10-dioxoanthracene) wherein the keto groups are located on the central ring. It is used as a digester additive to wood pulp for papermaking. Many anthraquinone derivatives are generated by organisms or synthesised industrially for use as dyes, pharmaceuticals, and catalysts. Anthraquinone is a yellow, highly crystalline solid, poorly soluble in water but soluble in hot organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble in ethanol near room temperature but 2.25 g will dissolve in 100 g of boiling ethanol. It is found in nature as the rare mineral hoelite.
- ^ a b c d Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. p. 3.28. ISBN 9781498754293.
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 724. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.