| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antimony | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | silvery lustrous gray | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(Sb) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antimony in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 51 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 15 (pnictogens) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 18, 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 903.78 K (630.63 °C, 1167.13 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 1908 K (1635 °C, 2975 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (at 20° C) | 6.694 g/cm3[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 6.53 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 19.79 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 193.43 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 25.23 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | common: −3, +3, +5 −2,? −1,? 0,[4] +1,? +2,? +4? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 140 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 139±5 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 206 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | rhombohedral (hR2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
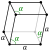
| Lattice constants | a = 0.45066 nm α = 57.112° ah = 0.43084 nm ch = 1.12736 nm (at 20 °C)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 11.04×10−6/K (at 20 °C)[a] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 24.4 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 417 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic[5] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −99.0×10−6 cm3/mol[6] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 55 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 20 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 42 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 3420 m/s (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 3.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 294–384 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-36-0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Arabic alchemists (before AD 815) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symbol | "Sb": from Latin stibium 'stibnite' | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of antimony | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Antimony is a chemical element; it has symbol Sb (from Latin stibium) and atomic number 51. A lustrous grey metal or metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient times and were powdered for use as medicine and cosmetics, often known by the Arabic name kohl.[8] The earliest known description of this metalloid in the West was written in 1540 by Vannoccio Biringuccio.
China is the largest producer of antimony and its compounds, with most production coming from the Xikuangshan Mine in Hunan. The industrial methods for refining antimony from stibnite are roasting followed by reduction with carbon, or direct reduction of stibnite with iron.
The most common applications for metallic antimony are in alloys with lead and tin, which have improved properties for solders, bullets, and plain bearings. It improves the rigidity of lead-alloy plates in lead–acid batteries. Antimony trioxide is a prominent additive for halogen-containing flame retardants. Antimony is used as a dopant in semiconductor devices.
- ^ "Standard Atomic Weights: Antimony". CIAAW. 1993.
- ^ Prohaska, Thomas; Irrgeher, Johanna; Benefield, Jacqueline; Böhlke, John K.; Chesson, Lesley A.; Coplen, Tyler B.; Ding, Tiping; Dunn, Philip J. H.; Gröning, Manfred; Holden, Norman E.; Meijer, Harro A. J. (4 May 2022). "Standard atomic weights of the elements 2021 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. doi:10.1515/pac-2019-0603. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ^ a b c Arblaster, John W. (2018). Selected Values of the Crystallographic Properties of Elements. Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International. ISBN 978-1-62708-155-9.
- ^ Anastas Sidiropoulos (2019). "Studies of N-heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Complexes of the Main Group Elements" (PDF). p. 39. doi:10.4225/03/5B0F4BDF98F60. S2CID 132399530.
- ^ Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). "Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds". CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (PDF) (86th ed.). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- ^ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.
- ^ Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
- ^ David Kimhi's Commentary on Isaiah 4:30 and I Chronicles 29:2; Hebrew: פוך/כְּחֻל, Aramaic: כּוּחְלִי/צדידא; Arabic: كحل, and which can also refer to antimony trisulfide. See also Z. Dori, Antimony and Henna (Heb. הפוך והכופר), Jerusalem 1983 (Hebrew).
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).