| Aphagia | |
|---|---|
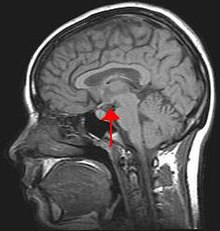 | |
| Arrow pointing to hypothalamus in human brain. The hypothalamus is responsible for controlling food intake and swallowing. | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
| Complications | Malnutrition, metabolic disorders |
Aphagia is the inability or refusal to swallow.[1][2] The word is derived from the Ancient Greek prefix α, meaning "not" or "without," and the suffix φαγία, derived from the verb φαγεῖν, meaning "to eat." It is related to dysphagia which is difficulty swallowing (Greek prefix δυσ, dys, meaning difficult, or defective), and odynophagia, painful swallowing (from ὀδύνη, odyn(o), meaning "pain"). Aphagia may be temporary or long term, depending on the affected organ. It is an extreme, life-threatening case of dysphagia. Depending on the cause, untreated dysphagia may develop into aphagia.