| Apheresis | |
|---|---|
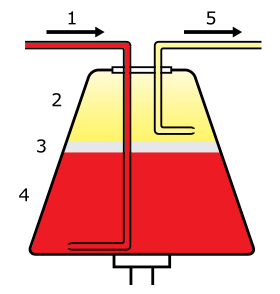 Whole blood enters the centrifuge (1) and separates into plasma (2), leukocytes (3), and erythrocytes (4). Selected components are then drawn off (5). | |
| MeSH | D016238 |
Apheresis (ἀφαίρεσις (aphairesis, "a taking away")) is a medical technology in which the blood of a person is passed through an apparatus that separates out one particular constituent and returns the remainder to the circulation. It is thus an extracorporeal therapy.
One of the uses of apheresis is for collecting hematopoetic stem cells.[1]
- ^ Katherine, Abel (2013). Official CPC Certification Study Guide. American Medical Association. p. 128.