This article should specify the language of its non-English content, using {{lang}}, {{transliteration}} for transliterated languages, and {{IPA}} for phonetic transcriptions, with an appropriate ISO 639 code. Wikipedia's multilingual support templates may also be used. (May 2019) |
| Arcadocypriot Greek | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | Arcadia, Cyprus | |||
| Era | c. 1300 – c. 300[citation needed] BC | |||
Indo-European
| ||||
Early forms | Proto-Greek
| |||
| Greek alphabet Cypriot syllabary | ||||
| Language codes | ||||
| ISO 639-3 | – | |||
grc-arc | ||||
| Glottolog | arca1234 | |||
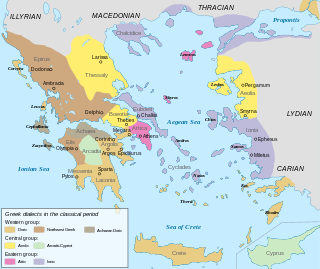 Distribution of Greek dialects in Greece in the classical period.[1]
| ||||
Arcadocypriot, or southern Achaean, was an ancient Greek dialect spoken in Arcadia in the central Peloponnese and in Cyprus. Its resemblance to Mycenaean Greek, as it is known from the Linear B corpus, indicates that they are closely related to it, and belong to the same dialect group, known as Achaean.[2]
In Cyprus the dialect was written using solely the Cypriot syllabary. The most extensive surviving text of the dialect is the Idalion Tablet.[3] A significant literary source on the vocabulary comes from the lexicon of 5th century AD grammarian Hesychius.
- ^ Roger D. Woodard (2008), "Greek dialects", in: The Ancient Languages of Europe, ed. R. D. Woodard, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, p. 51.
- ^ van Beek 2022, pp. 174, 182–184, 190
- ^ Georgiadou, Anna (2015). "The Tablet of Idalion (ICS 217)". Kyprios Character. History, Archaeology & Numismatics of Ancient Cyprus.