| Armenian | |
|---|---|
| հայերեն[a] | |
 "Armenian language" in the Armenian alphabet | |
| Pronunciation | [hɑjɛˈɾɛn] |
| Native to | |
| Ethnicity | Armenians |
Native speakers | 5.3 million[b] (2013–2021)[1] |
Indo-European
| |
Early forms | |
Standard forms | |
| Dialects | |
| Official status | |
Official language in |
|
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | hy |
| ISO 639-2 | arm (B) hye (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | Variously:hye – Eastern Armenianhyw – Western Armenianxcl – Classical Armenianaxm – Middle Armenian |
| Glottolog | arme1241 |
| Linguasphere | 57-AAA-a |
 The current distribution of the Armenian language in the southern Caucasus | |
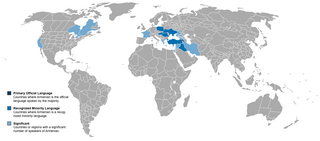 Official language spoken by the majority
Recognized minority language
Significant number of speakers | |
Armenian (endonym: հայերեն,[a] hayeren, pronounced [hɑjɛˈɾɛn]) is an Indo-European language and the sole member of the independent branch of the Armenian language family. It is the native language of the Armenian people and the official language of Armenia. Historically spoken in the Armenian highlands, today Armenian is also widely spoken throughout the Armenian diaspora. Armenian is written in its own writing system, the Armenian alphabet, introduced in 405 AD by Saint Mesrop Mashtots. The estimated number of Armenian speakers worldwide is between five and seven million.[20][21]
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Eastern Armenian at Ethnologue (26th ed., 2023)

Western Armenian at Ethnologue (26th ed., 2023)
Classical Armenian at Ethnologue (26th ed., 2023)
Middle Armenian at Ethnologue (26th ed., 2023)
- ^ "Treaty on Eurasian Economic Union" (PDF). eaeunion.org. Eurasian Economic Union. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 February 2021.
Article 110 Working Language of the Bodies of the Union. Language of International Treaties within the Union and Decisions of the Commission: 2. International treaties within the Union and decisions of the Commission that are binding on the Member States shall be adopted in Russian with subsequent translation into the official languages of the Member States, if it is provided for by their legislation, in the procedure determined by the Commission.
- ^ "Եվրասիական տնտեսական միություն". eaeunion.org (in Armenian). Eurasian Economic Union. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- ^ "Եվրասիական Տնտեսական Հանձնաժողով". eurasiancommission.org (in Armenian). Eurasian Economic Commission. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- ^ "Western Armenian – Cypriot Arabic: new century, new speakers?". ec.europa.eu. European Commission. 21 February 2017.
Dedicated to the two officially recognized minority languages of Cyprus, the event will focus on the teaching aspect of Western Armenian and Cypriot Arabic as mother tongues.
- ^ Hadjilyra, Alexander – Michael. "The Armenians of Cyprus" (PDF). publications.gov.cy. Press and Information Office, Republic of Cyprus. p. 15. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 December 2019.
According to the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages of the Council of Europe, Armenian was recognised as a minority language of Cyprus as of 1 December 2002.
- ^ Kenesei, István (2009). "Minority languages in Hungary" (PDF). efnil.org. European Federation of National Institutions for Language. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 December 2019.
As far as indigenous (autochthonous) minority languages are concerned, Hungarian legislation acknowledges the languages in the following list ...: Armenian, Boyash, Bulgarian, Croatian, German, Greek, Polish, Romani, Romanian, Ruthenian, Serbian, Slovak, Slovene, Ukrainian, and Hungarian Sign Language (HSL).
- ^ "Iraqi Constitution: Article 4" (PDF). The Republic of Iraq Ministry of Interior General Directorate for Nationality. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 November 2016. Retrieved 16 June 2014.
The right of Iraqis to educate their children in their mother tongue, such as Turkmen, Syriac, and Armenian shall be guaranteed in government educational institutions in accordance with educational guidelines, or in any other language in private educational institutions.
- ^ Zych, Maciej. "New Polish legislation regarding national, ethnic and linguistic minorities" (PDF). gugik.gov.pl. Head Office of Geodesy and Cartography of Poland. p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 December 2019.
There are 9 national minorities: Belorussian, Czech, Lithuanian, German, Armenian, Russian, Slovak, Ukrainian and Jewish; and 4 ethnic minorities – Karait, Lemko, Roma and Tartar.
- ^ Pisarek, Walery (2009). "The relationship between official and minority languages in Poland" (PDF). efnil.org. European Federation of National Institutions for Language. p. 118. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 December 2019.
In a Statement made by the Republic of Poland with relation to the ratification of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, Belarusian, Czech, Hebrew, Yiddish, Karaim, Kashubian, Lithuanian, Lemkian, German, Armenian, Romani, Russian, Slovak, Tatar and Ukrainian were recognized as minority languages.
- ^ Saramandu, Nicolae; Nevaci, Manuela (2009). "MULTILINGVISM ȘI LIMBI MINORITARE ÎN ROMÂNIA [MULTILINGUALISM AND MINORITY LANGUAGES IN ROMANIA]" (PDF) (in Romanian). Institute of Linguistics "Iorgu Iordan – Alexandru Rosetti", Romanian Academy. p. 25. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-12-14. Retrieved 2019-12-14.
În cazul României, 10 limbi beneficiază de protecție generală (albaneză, armeană, greacă, italiană, idiș, macedoneană, poloneză, romani, ruteană, tătară) și 10 limbi beneficiază de protecție sporită (bulgară, cehă, croată, germană, maghiară, rusă, sârbă, slovacă, turcă, ucraineană).
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Toktaş2006was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Bayır2013was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
HRWLanguageRightswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Uzum2017was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Law of Ukraine "On Principles of State Language Policy" (Current version – Revision from 01.02.2014)". Document 5029-17, Article 7: Regional or minority languages Ukraine, Paragraph 2 (in Ukrainian). rada.gov.ua. 1 February 2014. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
Стаття 7. Регіональні мови або мови меншин України ... 2. У контексті Європейської хартії регіональних мов або мов меншин до регіональних мов або мов меншин України, до яких застосовуються заходи, спрямовані на використання регіональних мов або мов меншин, що передбачені у цьому Законі, віднесені мови: російська, білоруська, болгарська, вірменська, гагаузька, ідиш, кримськотатарська, молдавська, німецька, новогрецька, польська, ромська, румунська, словацька, угорська, русинська, караїмська, кримчацька.
- ^ "H. Acharian Institute of Language". sci.am. Archived from the original on 5 October 2014.
Main Fields of Activity: investigation of the structure and functioning, history and comparative grammar of the Armenian language, exploration of the literary Eastern and Western Armenian Language, dialectology, regulation of literary language, development of terminology
- ^ Borjian, Maryam (2017). Language and Globalization: An Autoethnographic Approach. Routledge. p. 205. ISBN 9781315394619.
At the forefront of the development of Western Armenian in everyday life as well as in arts and technology is the Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation.
- ^ Yesayan, Catherine (June 19, 2019). "Unraveling the Life of Calouste Gulbenkian". Asbarez. Archived from the original on 2 May 2021.
The 'core' activity of the Armenian Department is the preservation, advancement and revitalization of Western Armenian.
- ^ Martirosyan, Hrach (March 2, 2020). "All You Need to Know about Armenian Language". aspirantum.com. ASPIRANTUM: Armenian School of Languages and Cultures. Archived from the original on 2 May 2021.
The total number of Armenians in the world is roughly estimated as 7–11 million, of which ca. 5-5.5 million speak Armenian.
- ^ "Language Monday: Armenian". World Book Encyclopedia. April 23, 2018. Archived from the original on 2 May 2021.
About 7 million people speak the Armenian language worldwide.