| Arrhythmia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Cardiac arrhythmia, heart arrhythmia, dysrhythmia, irregular heartbeat |
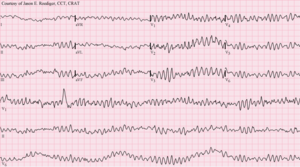 | |
| Ventricular fibrillation (VF) showing disorganized electrical activity producing a spiked tracing on an electrocardiogram (ECG) | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| Symptoms | Palpitations, dizziness or lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath, chest pain,[1] decreased level of consciousness |
| Complications | Stroke, heart failure[2][3] |
| Usual onset | Older age[4] |
| Types | Extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias, bradyarrhythmias[3] |
| Causes | Problems with the electrical conduction system of the heart[2] |
| Diagnostic method | Electrocardiogram, Holter monitor[5] |
| Treatment | Medications, medical procedures (pacemaker), surgery[6] |
| Frequency | Millions[4] |
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow.[2] A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia.[2] Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms.[1] Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats.[1] In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath, chest pain, or decreased level of consciousness.[1] While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure.[2][3] Others may result in sudden death.[3]
Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias.[3] Extra beats include premature atrial contractions, premature ventricular contractions and premature junctional contractions.[3] Supraventricular tachycardias include atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.[3] Ventricular arrhythmias include ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia.[3][7] Bradyarrhythmias are due to sinus node dysfunction or atrioventricular conduction disturbances.[8] Arrhythmias are due to problems with the electrical conduction system of the heart.[2] A number of tests can help with diagnosis, including an electrocardiogram (ECG) and Holter monitor.[5]
Many arrhythmias can be effectively treated.[2] Treatments may include medications, medical procedures such as inserting a pacemaker, and surgery.[6] Medications for a fast heart rate may include beta blockers, or antiarrhythmic agents such as procainamide, which attempt to restore a normal heart rhythm.[6] This latter group may have more significant side effects, especially if taken for a long period of time.[6] Pacemakers are often used for slow heart rates.[6] Those with an irregular heartbeat are often treated with blood thinners to reduce the risk of complications.[6] Those who have severe symptoms from an arrhythmia or are medically unstable may receive urgent treatment with a controlled electric shock in the form of cardioversion or defibrillation.[6]
Arrhythmia affects millions of people.[4] In Europe and North America, as of 2014, atrial fibrillation affects about 2% to 3% of the population.[9] Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter resulted in 112,000 deaths in 2013, up from 29,000 in 1990.[10] However, in most recent cases concerning the SARS-CoV‑2 pandemic, cardiac arrhythmias are commonly developed and associated with high morbidity and mortality among patients hospitalized with the COVID-19 infection, due to the infection's ability to cause myocardial injury.[11] Sudden cardiac death is the cause of about half of deaths due to cardiovascular disease and about 15% of all deaths globally.[12] About 80% of sudden cardiac death is the result of ventricular arrhythmias.[12] Arrhythmias may occur at any age but are more common among older people.[4] Arrhythmias may also occur in children; however, the normal range for the heart rate varies with age.[3]
- ^ a b c d "What Are the Signs and Symptoms of an Arrhythmia?". National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g "What Is Arrhythmia?". National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011. Archived from the original on 2 March 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Types of Arrhythmia". National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011. Archived from the original on 7 June 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ a b c d "Who Is at Risk for an Arrhythmia?". National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011. Archived from the original on 3 March 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ a b "How Are Arrhythmias Diagnosed?". National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011. Archived from the original on 18 February 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g "How Are Arrhythmias Treated?". National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011. Archived from the original on 17 February 2015. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ Martin CA, Matthews GD, Huang CL (April 2012). "Sudden cardiac death and inherited channelopathy: the basic electrophysiology of the myocyte and myocardium in ion channel disease". Heart. 98 (7): 536–543. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2011-300953. PMC 3308472. PMID 22422742.
- ^ Vogler J, Breithardt G, Eckardt L (July 2012). "Bradyarrhythmias and conduction blocks". Revista Espanola de Cardiologia. 65 (7): 656–667. doi:10.1016/j.rec.2012.01.027. PMID 22627074. S2CID 18983179.
- ^ Zoni-Berisso M, Lercari F, Carazza T, Domenicucci S (2014). "Epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: European perspective". Clinical Epidemiology. 6: 213–220. doi:10.2147/CLEP.S47385. PMC 4064952. PMID 24966695.
- ^ Naghavi M, Wang H, Lozano R, Davis A, Liang X, Zhou M, et al. (GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators) (January 2015). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. 385 (9963): 117–171. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604. PMID 25530442.
- ^ Kuck KH (June 2020). "Arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in the COVID-19 pandemic". Herz. 45 (4): 325–326. doi:10.1007/s00059-020-04924-0. PMC 7181098. PMID 32333026.
- ^ a b Mehra R (2007). "Global public health problem of sudden cardiac death". Journal of Electrocardiology. 40 (6 Suppl): S118–S122. doi:10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2007.06.023. PMID 17993308.
