| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Arsoric acid[1]
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.001 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1553, 1554 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
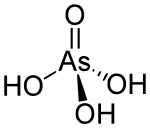
| H3AsO4 | |
| Molar mass | 141.942 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White translucent or colorless crystals, hygroscopic |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 35.5 °C (95.9 °F; 308.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) decomposes |
| 16.7 g/(100 mL) | |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol |
| Vapor pressure | 55 hPa (50 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa1 = 2.19 pKa2 = 6.94 pKa3 = 11.5[2] |
| Conjugate base | Arsenate |
| Structure | |
| Tetrahedral at arsenic atom | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Extremely toxic, carcinogenic, corrosive |
| GHS labelling: | |
    
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H312, H314, H331, H350, H361, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P281, P301+P310, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P310, P311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
48 mg/kg (rat, oral)
6 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Sodium arsenate |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Arsenic acid or arsoric acid is the chemical compound with the formula H3AsO4. More descriptively written as AsO(OH)3, this colorless acid is the arsenic analogue of phosphoric acid. Arsenate and phosphate salts behave very similarly. Arsenic acid as such has not been isolated, but is only found in solution, where it is largely ionized. Its hemihydrate form (2H3AsO4·H2O) does form stable crystals. Crystalline samples dehydrate with condensation at 100 °C.[3]
- ^ "Arsenic acid".
- ^ Perrin, D. D., ed. (1982) [1969]. Ionisation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases in Aqueous Solution. IUPAC Chemical Data (2nd ed.). Oxford: Pergamon (published 1984). Entry 11. ISBN 0-08-029214-3. LCCN 82-16524.
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. (2001). Inorganic Chemistry. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
