
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Arsenic trisulfide | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.744 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| As2S3 | |
| Molar mass | 246.02 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow or orange crystals |
| Density | 3.43 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 310 °C (590 °F; 583 K) |
| Boiling point | 707 °C (1,305 °F; 980 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in ammonia |
| −70.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
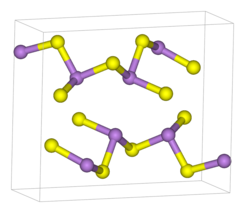
| Structure[1] | |
| monoclinic | |
| P21/n (No. 11) | |
a = 1147.5(5) pm, b = 957.7(4) pm, c = 425.6(2) pm α = 90°, β = 90.68(8)°, γ = 90°
| |
| pyramidal (As) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[3][4] | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H300, H331, H400, H411 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
[1910.1018] TWA 0.010 mg/m3[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca C 0.002 mg/m3 [15-minute][2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [5 mg/m3 (as As)][2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Arsenic trisulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula As2S3. It is a dark yellow solid that is insoluble in water. It also occurs as the mineral orpiment (Latin: auripigmentum), which has been used as a pigment called King's yellow. It is produced in the analysis of arsenic compounds. It is a group V/VI, intrinsic p-type semiconductor and exhibits photo-induced phase-change properties.[clarification needed]
- ^ Mullen, D. J. E.; Nowacki, W (1972), "Refinement of the crystal structures of realgar, AsS and orpiment, As2S3" (PDF), Z. Kristallogr., 136 (1–2): 48–65, Bibcode:1972ZK....136...48M, doi:10.1524/zkri.1972.136.1-2.48.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0038". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Index no. 033-002-00-5 of Annex VI, Part 3, to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. OJEU L353, 31.12.2008, pp 1–1355 at p 427.
- ^ "Arsenic, inorganic compounds (as As)", 29 C.F.R. § 1910.1018, 58 FR 35310, June 30, 1993, as amended. "Arsenic (inorganic compounds, as As)", Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (NIOSH) Publication No. 2005-149, Washington, DC: Government Printing Office, 2005, ISBN 9780160727511.
