| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1H-Arsole | |||
| Other names
Arsenole
Arsacyclopentadiene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H4AsH | |||
| Molar mass | 128.00 g mol−1 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Pyrrole, phosphole, bismole, stibole | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
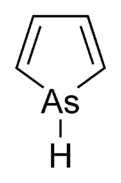
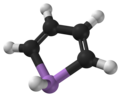
Arsole, also called arsenole[1] or arsacyclopentadiene, is an organoarsenic compound with the formula C4H4AsH. It is classified as a metallole and is isoelectronic to and related to pyrrole except that an arsenic atom is substituted for the nitrogen atom. Whereas the pyrrole molecule is planar, the arsole molecule is not, and the hydrogen atom bonded to arsenic extends out of the molecular plane. Arsole is only moderately aromatic, with about 40% the aromaticity of pyrrole.[2] Arsole itself has not been reported in pure form, but several substituted analogs called arsoles exist. Arsoles and more complex arsole derivatives have similar structure and chemical properties to those of phosphole derivatives. When arsole is fused to a benzene ring, this molecule is called arsindole, or benzarsole.[3]
- ^ Mann 1970: "In English this ring system has frequently named arsenole 'for euphony'."
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
revwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ A. Muranaka; S. Yasuike; C.-Y. Liu; J. Kurita; N. Kakusawa; T. Tsuchiya; M. Okuda; N. Kobayashi; Y. Matsumoto; K. Yoshida; D. Hashizume; M. Uchiyama (2009). "Effect of Periodic Replacement of the Heteroatom on the Spectroscopic Properties of Indole and Benzofuran Derivatives". J. Phys. Chem. A. 113 (2): 464–473. doi:10.1021/jp8079843. PMID 19099440.