 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Many[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular[2] Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.189.847 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
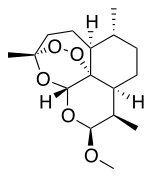
| Formula | C16H26O5 |
| Molar mass | 298.379 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 86 to 88 °C (187 to 190 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Artemether is a medication used for the treatment of malaria.[1][2] The injectable form is specifically used for severe malaria rather than quinine.[2] In adults, it may not be as effective as artesunate.[2] It is given by injection in a muscle.[2] It is also available by mouth in combination with lumefantrine, known as artemether/lumefantrine.[1][3]
Artemether causes relatively few side effects.[4] An irregular heartbeat may rarely occur.[4] While there is evidence that use during pregnancy may be harmful in animals, there is no evidence of concern in humans.[4] The World Health Organization (WHO) therefore recommends its use during pregnancy.[4] It is in the artemisinin class of medication.[4]
Artemether has been studied since at least 1981, and has been in medical use since 1987.[5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6]
- ^ a b c "Artemether and Lumefantrine (Monograph)". Drugs.com. 22 February 2023. Retrieved 17 February 2024.
- ^ a b c d e Esu EB, Effa EE, Opie ON, Meremikwu MM (June 2019). "Artemether for severe malaria". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 6 (6): CD010678. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010678.pub3. PMC 6580442. PMID 31210357.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Coartem FDA labelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e Kovacs SD, Rijken MJ, Stergachis A (February 2015). "Treating severe malaria in pregnancy: a review of the evidence". Drug Safety. 38 (2): 165–181. doi:10.1007/s40264-014-0261-9. PMC 4328128. PMID 25556421.
- ^ Rao Y, Zhang D, Li R (2016). Tu Youyou and the Discovery of Artemisinin: 2015 Nobel Laureate in Physiology or Medicine. World Scientific. p. 162. ISBN 9789813109919. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
- ^ World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2019. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.