| Arthritis | |
|---|---|
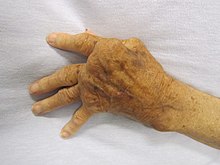 | |
| A hand affected by rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune form of arthritis | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Rheumatology |
| Symptoms | Joint pain, stiffness, redness, swelling, decreased range of motion[2][3] |
| Complications | Amplified musculoskeletal pain syndrome[4] |
| Types | > 100, most common (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis)[5][6][7] |
| Risk factors | Family history, age, sex trait, previous joint injury, obesity.[8] |
| Treatment | Resting, applying ice or heat, weight loss, exercise, joint replacement[7] |
| Medication | Ibuprofen, paracetamol (acetaminophen)[9] |
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints.[2] Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness.[2] Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints.[2][3] In some types of arthritis, other organs are also affected.[7] Onset can be gradual or sudden.[6]
There are over 100 types of arthritis.[10][5][6] The most common forms are osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease) and rheumatoid arthritis.[7] Osteoarthritis usually occurs with age and affects the fingers, knees, and hips.[7][11] Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the hands and feet.[7] Other types include gout, lupus, fibromyalgia, and septic arthritis.[7][12] They are all types of rheumatic disease.[2]
Treatment may include resting the joint and alternating between applying ice and heat.[7][13] Weight loss and exercise may also be useful.[7][14] Recommended medications may depend on the form of arthritis.[15][9] These may include pain medications such as ibuprofen and paracetamol (acetaminophen).[9] In some circumstances, a joint replacement may be useful.[7]
Osteoarthritis affects more than 3.8% of people, while rheumatoid arthritis affects about 0.24% of people.[16] Gout affects about 1–2% of the Western population at some point in their lives.[17] In Australia about 15% of people are affected by arthritis,[18] while in the United States more than 20% have a type of arthritis.[12][19] Overall the disease becomes more common with age.[12] Arthritis is a common reason that people miss work and can result in a decreased quality of life.[9] The term is derived from arthr- (meaning 'joint') and -itis (meaning 'inflammation').[20][21]
- ^ "arthritis noun - Definition, pictures, pronunciation and usage notes Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary". www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ^ a b c d e "Arthritis and Rheumatic Diseases". NIAMS. October 2014. Archived from the original on 4 October 2016. Retrieved 31 March 2021.
- ^ a b "Arthritis Types". CDC. 22 June 2016. Archived from the original on 14 September 2016. Retrieved 14 September 2016.
- ^ "Amplified Musculoskeletal Pain Syndrome (AMPS)". Children's Health.
- ^ a b Athanasiou KA, Darling EM, Hu JC, DuRaine GD, Reddi AH (2013). Articular Cartilage. CRC Press. p. 105. ISBN 9781439853252.
- ^ a b c "Arthritis Basics". CDC. 9 May 2016. Archived from the original on 17 September 2016. Retrieved 14 September 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Living With Arthritis: Health Information Basics for You and Your Family". NIAMS. July 2014. Archived from the original on 4 October 2016. Retrieved 14 September 2016.
- ^ "Arthritis – Overview". mayoclinic.org. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 6 June 2022.
- ^ a b c d "Arthritis: An Overview". OrthoInfo. October 2007. Archived from the original on 19 September 2016. Retrieved 14 September 2016.
- ^ Clegg HB, Jackson L (2013). Eating well to fight arthritis: 200 easy recipes and practical tips to help reduce inflammation and ease symptoms. Favorite Recipes Press. ISBN 978-0-9815640-5-0. OCLC 854909375.
- ^ "Traditional Chinese Medicine Formula in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis of Knees or Hips". Case Medical Research. 1 October 2019. doi:10.31525/ct1-nct04110847. ISSN 2643-4652. S2CID 242704843.
- ^ a b c "Arthritis". CDC. 22 July 2015. Archived from the original on 22 September 2016. Retrieved 14 September 2016.
- ^ SIDE EFFECTS MAY INCLUDE STRANGERS, McGill-Queen's University Press, 22 October 2020, p. 27, doi:10.2307/j.ctv1ghv4jh.24, S2CID 243669150
- ^ "Blood-pressure pill may also aid weight loss". New Scientist. 198 (2654): 16. May 2008. doi:10.1016/s0262-4079(08)61076-3. ISSN 0262-4079.
- ^ "Higher-than-recommended doses of antipsychotic medications may not benefit people with schizophrenia and may increase side effects". PsycEXTRA Dataset. 2007. doi:10.1037/e603782007-025.
- ^ March L, Smith EU, Hoy DG, Cross MJ, Sanchez-Riera L, Blyth F, et al. (June 2014). "Burden of disability due to musculoskeletal (MSK) disorders". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Rheumatology. 28 (3): 353–366. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2014.08.002. PMID 25481420.
- ^ Richette P, Bardin T (January 2010). "Gout". Lancet. 375 (9711): 318–328. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60883-7. PMID 19692116. S2CID 208793280.
- ^ "National Health Survey". ABS. 8 December 2015. Archived from the original on 16 January 2017. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ^ Pirotta M (September 2010). "Arthritis disease - the use of complementary therapies". Australian Family Physician. 39 (9): 638–640. PMID 20877766.
- ^ Waite M, ed. (2012). Paperback Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 35. ISBN 9780199640942. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016.
- ^ Leonard C (2015). Quick & Easy Medical Terminology - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 160. ISBN 9780323370646.