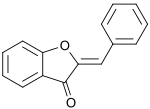
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Benzylidene-1-benzofuran-3(2H)-one | |
| Other names
2-Benzylidenebenzofuran-3(2H)-one
2-Benzylidene-1-benzofuran-3-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 222.243 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
An aurone is a heterocyclic chemical compound, which is a type of flavonoid.[1] There are two isomers of the molecule, with (E)- and (Z)-configurations. The molecule contains a benzofuran element associated with a benzylidene linked in position 2. In aurone, a chalcone-like group is closed into a 5-membered ring instead of the 6-membered ring more typical of flavonoids.
- ^ Nakayama, T (2002). "Enzymology of aurone biosynthesis". Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering. 94 (6): 487–91. doi:10.1016/S1389-1723(02)80184-0. PMID 16233339.