| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
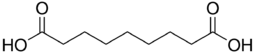
| Preferred IUPAC name
Nonanedioic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1101094 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.246 |
| EC Number |
|
| 261342 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H16O4 | |
| Molar mass | 188.22 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.443 g/mL |
| Melting point | 109 to 111 °C (228 to 232 °F; 382 to 384 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 286 °C (547 °F; 559 K) at 100 mmHg[1] |
| 2.14 g/L[2] | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.550, 5.498[2] |
| Pharmacology | |
| D10AX03 (WHO) | |
| Topical | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| Very low | |
| 12 h | |
| Legal status | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319 | |
| P264, P280, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Azelaic acid (AzA) is an organic compound with the formula HOOC(CH2)7COOH.[3] This saturated dicarboxylic acid exists as a white powder. It is found in wheat, rye, and barley. It is a precursor to diverse industrial products including polymers and plasticizers, as well as being a component of a number of hair and skin conditioners.[4] AzA inhibits tyrosinase.[5]
- ^ a b Sigma-Aldrich catalog Archived April 9, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Bretti, C.; Crea, F.; Foti, C.; Sammartano, S. (2006). "Solubility and Activity Coefficients of Acidic and Basic Nonelectrolytes in Aqueous Salt Solutions. 2. Solubility and Activity Coefficients of Suberic, Azelaic, and Sebacic Acids in NaCl(aq), (CH3)4NCl(aq), and (C2H5)4NI(aq) at Different Ionic Strengths and at t = 25 °C". J. Chem. Eng. Data. 51 (5): 1660–1667. doi:10.1021/je060132t.
- ^ Del Rosso, James Q. (2006-02-01). "The use of topical azelaic acid for common skin disorders other than inflammatory rosacea". Cutis. 77 (2 Suppl): 22–24. ISSN 0011-4162. PMID 16566285.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Boywas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
TyrosinaseInhibitorwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).