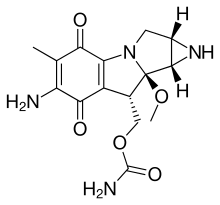
In organic chemistry, aziridines are organic compounds containing the aziridine functional group (chemical structure (R−)4C2N−R), a three-membered heterocycle with one amine (>NR) and two methylene bridges (>CR2).[2][3][4] The parent compound is aziridine (or ethylene imine), with molecular formula C2H4NH. Several drugs feature aziridine rings, including mitomycin C, porfiromycin, and azinomycin B (carzinophilin).[5]
- ^ Tomasz, Maria (September 1995). "Mitomycin C: small, fast and deadly (but very selective)". Chemistry and Biology. 2 (9): 575–579. doi:10.1016/1074-5521(95)90120-5. PMID 9383461.
- ^ Gilchrist, T.L. (1987). Heterocyclic chemistry. ISBN 978-0-582-01421-3.
- ^ Epoxides and Aziridines – A Mini Review Albert Padwa and S. Shaun Murphree Arkivoc (JC-1522R) pp. 6–33 Online article
- ^ Sweeney, J. B. (2002). "Aziridines: Epoxides' ugly cousins?". Chem. Soc. Rev. 31 (5): 247–258. doi:10.1039/B006015L. PMID 12357722.
- ^ Ismail, Fyaz M.D.; Levitsky, Dmitri O.; Dembitsky, Valery M. (2009). "Aziridine alkaloids as potential therapeutic agents". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 44 (9): 3373–3387. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2009.05.013. PMID 19540628.