| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Carbamoyliminourea
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.229 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E927a (glazing agents, ...) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
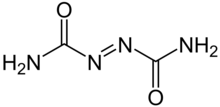
| C2H4N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 116.080 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow to orange/red crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H242, H331, H334 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | [1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Azodicarbonamide, ADCA, ACA,[1] ADA, or azo(bis)formamide, is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C2H4O2N4.[2] It is a yellow to orange-red, odorless, crystalline powder. It is sometimes called a 'yoga mat' chemical because of its widespread use in foamed plastics.[3][4] It was first described by John Bryden in 1959.[5]
- ^ Farah, Troy (28 May 2019). "Banned bread: why does the US allow additives that Europe says are unsafe?". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ "Azodicarbonamide (CICADS)". Inchem. International Programme on Chemical Safety. Archived from the original on 24 August 2010. Retrieved 14 August 2010. Also published by World Health Organization, Geneva, 1999.
- ^ Arts, Josje; Kimber, Ian (October 2017). "Azodicarbonamide (ADCA): A reconsideration of classification as a respiratory sensitiser". Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology. 89: 268–278. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2017.07.018. PMID 28734852.
- ^ "Almost 500 Foods Contain the 'Yoga Mat' Compound. Should We Care?". NPR.
- ^ Bryden, J. H. (10 January 1961). "The crystal structure of azodicarbonamide". Acta Crystallographica. 14 (1): 61–63. Bibcode:1961AcCry..14...61B. doi:10.1107/S0365110X61000139.
