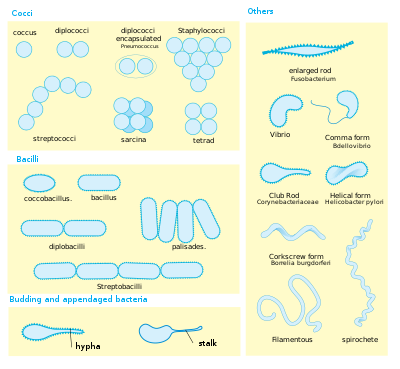
Bacterial cellular morphologies are the shapes that are characteristic of various types of bacteria and often key to their identification. Their direct examination under a light microscope enables the classification of these bacteria (and archaea).
Generally, the basic morphologies are spheres (coccus) and round-ended cylinders or rod shaped (bacillus). But, there are also other morphologies such as helically twisted cylinders (example Spirochetes), cylinders curved in one plane (selenomonads) and unusual morphologies (the square, flat box-shaped cells of the Archaean genus Haloquadratum). Other arrangements include pairs, tetrads, clusters, chains and palisades.