| Balinese | |
|---|---|
| ᬪᬵᬱᬩᬮᬶ / ᬩᬲᬩᬮᬶ1 Bhāṣa Bali / Basä bali1 | |
| Native to | Indonesia |
| Region | Bali, Nusa Penida, Lombok |
| Ethnicity | |
Native speakers | 3.3 million (2000 census)[1] |
Early form | |
| Dialects | |
| Latin script Balinese script | |
| Official status | |
| Regulated by | Lembaga Bahasa, Aksara dan Sastra Bali[3] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | ban |
| ISO 639-3 | ban |
| Glottolog | bali1278 |
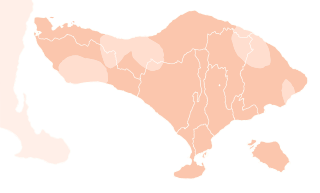 Balinese is the majority language where vast majority are first language speakers
Balinese is the majority language, with other languages being spoken largely or as a second language (such as Javanese, Sasak, and Malay)
Balinese is a minority language | |
Balinese is an Austronesian language spoken on the Indonesian island of Bali, as well as Northern Nusa Penida, Western Lombok,[4] Southern Sumatra, and Sulawesi.[5] Most Balinese speakers also use Indonesian. The 2000 national census recorded 3.3 million people speakers of Balinese, however the Bali Cultural Agency estimated in 2011 that the number of people still using the Balinese language in their daily lives is under 1 million. The language has been classified as "not endangered" by Glottolog.[2]
The higher registers of the language borrow extensively from Javanese: an old form of classical Javanese, Kawi, is used in Bali as a religious and ceremonial language.
- ^ Balinese at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ a b "Glottolog 4.3 - Balinese". glottolog.org. Retrieved 2021-04-27.
- ^ Peraturan Daerah Provinsi Bali No 1 Tahun 2018 Tentang Bahasa, Aksara, Dan Sastra Bali (Regional Regulation 1, Article 12) (in Indonesian). 2018.
- ^ Ethnologue.
- ^ Clynes, Adrian (1995). Topics in the Phonology and Morphosyntax of Balinese (PhD thesis). Australian National University. doi:10.25911/5d77865d38e15. hdl:1885/10744.