This article may have too many section headers. (March 2023) |
| Barotrauma | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Squeeze, decompression illness, lung overpressure injury, volutrauma |
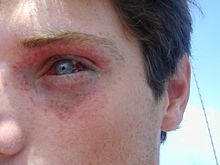 | |
| Mild barotrauma to a diver caused by mask squeeze. Eye and surrounding skin show petechiae and a subconjunctival haemmorhage. | |
| Symptoms | Dependent on location |
| Complications | Arterial gas embolism, pneumothorax, mediastinal emphysema |
| Causes | Pressure difference between the environment and a gas-filled space in or in contact with the affected tissues |
Barotrauma is physical damage to body tissues caused by a difference in pressure between a gas space inside, or in contact with, the body and the surrounding gas or liquid.[1][2] The initial damage is usually due to over-stretching the tissues in tension or shear, either directly by an expansion of the gas in the closed space or by pressure difference hydrostatically transmitted through the tissue. Tissue rupture may be complicated by the introduction of gas into the local tissue or circulation through the initial trauma site, which can cause blockage of circulation at distant sites or interfere with the normal function of an organ by its presence. The term is usually applied when the gas volume involved already exists prior to decompression. Barotrauma can occur during both compression and decompression events.[1][2]
Barotrauma generally manifests as sinus or middle ear effects, lung overpressure injuries and injuries resulting from external squeezes. Decompression sickness is indirectly caused by ambient pressure reduction, and tissue damage is caused directly and indirectly by gas bubbles. However, these bubbles form out of supersaturated solution from dissolved gases, and are not generally considered barotrauma. Decompression illness is a term that includes decompression sickness and arterial gas embolism caused by lung overexpansion barotrauma. It is also classified under the broader term of dysbarism, which covers all medical conditions resulting from changes in ambient pressure.[3]
Barotrauma typically occurs when the organism is exposed to a significant change in ambient pressure, such as when a scuba diver, a free-diver or an airplane passenger ascends or descends or during uncontrolled decompression of a pressure vessel such as a diving chamber or pressurized aircraft, but can also be caused by a shock wave. Ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) is a condition caused by over-expansion of the lungs by mechanical ventilation used when the body is unable to breathe for itself and is associated with relatively large tidal volumes and relatively high peak pressures. Barotrauma due to overexpansion of an internal gas-filled space may also be termed volutrauma.