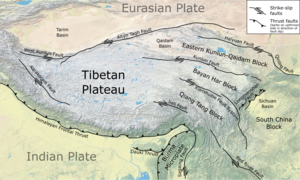
The Bayan Har block or Bayan Kola block is an elongate wedge-shaped block that forms part of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. It is bounded to the southeast by the Longmenshan Fault, a major thrust fault zone, which forms the active tectonic boundary between the plateau and the Sichuan Basin. To the northeast, the boundary is formed by the Kunlun and Minjiang Faults juxtaposing the block against the Eastern Kunlun-Qaidam block[1] and to the southwest by the Xianshuihe fault system forms its boundary with the Qiangtang block.[2] All of these are major left-lateral strike-slip fault zones. The block is currently moving to the southeast relative to the South China block.[3][4]
- ^ Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Freymueller, J.T.; Li, Z. (2017). "Probing Coulomb stress triggering effects for a Mw > 6.0 earthquake sequence from 1997 to 2014 along the periphery of the Bayan Har block on the Tibetan Plateau". Tectonophysics. 694: 249–267. Bibcode:2017Tectp.694..249W. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2016.11.009.
- ^ Xu, C.; Xu, X.; Shyu, J.B.H.; Gao, M.; Tan, X.; Ran, Y.; Zheng, W. (2015). "Landslides triggered by the 20 April 2013 Lushan, China, Mw 6.6 earthquake from field investigations and preliminary analyses". Landslides. 12 (2): 365–385. doi:10.1007/s10346-014-0546-1. S2CID 129486468.
- ^ Xu, X.W.; Wen, X.Z.; Chen, G.H.; Yu, G.H. (2008). "Discovery of the Longriba Fault Zone in Eastern Bayan Har Block, China and its tectonic implication". Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences. 51 (9): 1209–1223. Bibcode:2008ScChD..51.1209X. doi:10.1007/s11430-008-0097-1. S2CID 128682470.
- ^ Yujun Sun, Taoyuan Fan, Chunjing Zhou, Zhonghai Wu (2015). "The Evolution of Stress and Strain around the Bayan Har Block in the Tibetan Plateau". Journal of Earthquakes. 2015: 10. doi:10.1155/2015/971628. 971628.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)