 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 100% |
| Protein binding | 96% |
| Metabolism | extensive |
| Elimination half-life | 3-4 hours[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.728 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
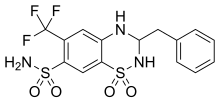
| Formula | C15H14F3N3O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 421.41 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Bendroflumethiazide, formerly bendrofluazide, trade name Aprinox, is a thiazide diuretic used to treat hypertension.
Bendroflumethiazide is a thiazide diuretic which works by inhibiting sodium reabsorption at the beginning of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT). Water is lost as a result of more sodium reaching the collecting ducts. Bendroflumethiazide has a role in the treatment of mild heart failure although loop diuretics are better for reducing overload. The main use of bendroflumethiazide currently is in hypertension (part of the effect is due to vasodilation).
It was patented in 1958 and approved for medical use in 1960.[3]
- ^ BNF 45 March 2003
- ^ Ed. Sean C. Sweetman (ed.). Martindale: The complete drug reference (33 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 456. ISBN 9783527607495.