 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Milgamma |
| Other names | S-Benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.906 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
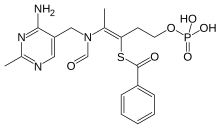
| Formula | C19H23N4O6PS |
| Molar mass | 466.45 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Benfotiamine (rINN, or S-benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate) is a synthetic, fat-soluble, S-acyl derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1) that is approved in some countries as a medication or dietary supplement to treat diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy. Benfotiamine was developed in late 1950s in Japan.[1][2]
- ^ Wada T, Takagi H, Minakami H, Hamanaka W, Okamoto K, Ito A, Sahashi Y (July 1961). "A new thiamine derivative, S-benzoylthiamine O-monophosphate". Science. 134 (3473): 195–196. Bibcode:1961Sci...134..195W. doi:10.1126/science.134.3473.195. PMID 13782394. S2CID 10384617.
- ^ Sambon M, Wins P, Bettendorff L (May 2021). "Neuroprotective Effects of Thiamine and Precursors with Higher Bioavailability: Focus on Benfotiamine and Dibenzoylthiamine". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 22 (11): 5418. doi:10.3390/ijms22115418. PMC 8196556. PMID 34063830.