| Bengal tiger | |
|---|---|

| |
| Adult male in Kanha Tiger Reserve, India | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Subfamily: | Pantherinae |
| Genus: | Panthera |
| Species: | P. tigris |
| Subspecies: | P. t. tigris |
| Population: | Bengal tiger |
| |
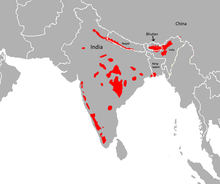
| Range of Bengal tiger in red | |
The Bengal tiger or Royal Bengal tiger is a population of the Panthera tigris tigris subspecies and the nominate tiger subspecies. It ranks among the biggest wild cats alive today. It is estimated to have been present in the Indian subcontinent since the Late Pleistocene for about 12,000 to 16,500 years. Its historical range covered the Indus River valley until the early 19th century, almost all of India, western Pakistan, southern Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan and southwestern China. Today, it inhabits India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and southwestern China. It is threatened by poaching, habitat loss and habitat fragmentation.
As of 2022, the Bengal tiger population was estimated at 3,167–3,682 individuals in India, 316–355 individuals in Nepal, 131 individuals in Bhutan and around 114 individuals in Bangladesh.