| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
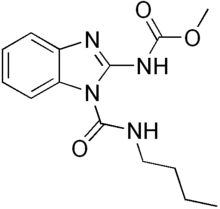
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(Butylcarbamoyl)-1H-1,3-benzimidazol-2-yl methylcarbamate | |
| Other names
Benomyl
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 825455 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.962 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3077 2757 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H18N4O3 | |
| Molar mass | 290.323 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid[1] |
| Odor | acrid[1] |
| Melting point | 290 °C (554 °F; 563 K) decomposes[1] |
| 0.0004% (20 °C)[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[2] | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H315, H317, H335, H340, H360, H410 | |
| P203, P261, P264, P271, P272, P273, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P316, P317, P318, P319, P321, P332+P317, P333+P317, P362+P364, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | noncombustible[1] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 15 mg/m3 (total) TWA 5 mg/m3 (resp)[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
none[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Benomyl (also marketed as Benlate) is a fungicide introduced in 1968 by DuPont. It is a systemic benzimidazole fungicide that is selectively toxic to microorganisms and invertebrates (especially earthworms), but relatively nontoxic toward mammals.[3]
Due to the prevalence of resistance of parasitic fungi to benomyl, it and similar pesticides are of diminished effectiveness. Nonetheless, it is widely used.
- ^ a b c d e f g h NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0048". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Benomyl". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ Franz Müller; Peter Ackermann; Paul Margot (2012). "Fungicides, Agricultural, 2. Individual Fungicides". Fungicides, Agricultural, 2. Individual Fungicides. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.o12_o06. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.