| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
N-Alkyl-N-benzyl-N,N-dimethylammonium chloride; Alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride; ADBAC; BC50 BC80
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| Properties | |
| Variable | |
| Molar mass | Variable |
| Appearance |
|
| Density | 0.98 g/cm3 |
| Very soluble | |
| Pharmacology | |
| D08AJ01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H312, H314, H410 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P273, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) (if solvent based) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
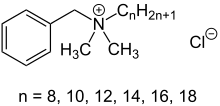
Benzalkonium chloride (BZK, BKC, BAK, BAC), also known as alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride (ADBAC) and by the trade name Zephiran,[1] is a type of cationic surfactant. It is an organic salt classified as a quaternary ammonium compound. ADBACs have three main categories of use: as a biocide, a cationic surfactant, and a phase transfer agent.[2] ADBACs are a mixture of alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chlorides, in which the alkyl group has various even-numbered alkyl chain lengths.
- ^ "Zephiran (benzalkonium chloride)" (PDF). Sanofi. Retrieved 28 April 2020.
- ^ Maximilian Lackner, Josef Peter Guggenbichler "Antimicrobial Surfaces" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2013. doi:10.1002/14356007.q03_q01
