| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzoic acid[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Benzenecarboxylic acid | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| 636131 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.562 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E210 (preservatives) | ||
| 2946 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | benzoic+acid | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H6O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 122.123 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless crystalline solid | ||
| Odor | Faint, pleasant odor | ||
| Density | 1.2659 g/cm3 (15 °C) 1.0749 g/cm3 (130 °C)[2] | ||
| Melting point | 122 °C (252 °F; 395 K)[7] | ||
| Boiling point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K)[7] | ||
| 1.7 g/L (0 °C) 2.7 g/L (18 °C) 3.44 g/L (25 °C) 5.51 g/L (40 °C) 21.45 g/L (75 °C) 56.31 g/L (100 °C)[2][3] | |||
| Solubility | Soluble in acetone, benzene, CCl4, CHCl3, alcohol, ethyl ether, hexane, phenyls, liquid ammonia, acetates | ||
| Solubility in methanol | 30 g/100 g (−18 °C) 32.1 g/100 g (−13 °C) 71.5 g/100 g (23 °C)[2] | ||
| Solubility in ethanol | 25.4 g/100 g (−18 °C) 47.1 g/100 g (15 °C) 52.4 g/100 g (19.2 °C) 55.9 g/100 g (23 °C)[2] | ||
| Solubility in acetone | 54.2 g/100 g (20 °C)[2] | ||
| Solubility in olive oil | 4.22 g/100 g (25 °C)[2] | ||
| Solubility in 1,4-dioxane | 55.3 g/100 g (25 °C)[2] | ||
| log P | 1.87 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 0.16 Pa (25 °C) 0.19 kPa (100 °C) 22.6 kPa (200 °C)[4] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | |||
| −70.28·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5397 (20 °C) 1.504 (132 °C)[2] | ||
| Viscosity | 1.26 mPa (130 °C) | ||
| Structure | |||
| Monoclinic | |||
| Planar | |||
| 1.72 D in dioxane | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
146.7 J/mol·K[4] | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
167.6 J/mol·K[2] | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−385.2 kJ/mol[2] | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−3228 kJ/mol[4] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Irritant | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  [8] [8]
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H318, H335[8] | |||
| P261, P280, P305+P351+P338[8] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 121.5 °C (250.7 °F; 394.6 K)[7] | ||
| 571 °C (1,060 °F; 844 K)[7] | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
1700 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | JT Baker | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other cations
|
Sodium benzoate, Potassium benzoate | ||
Related carboxylic acids
|
Hydroxybenzoic acids Aminobenzoic acids, Nitrobenzoic acids, Phenylacetic acid | ||
Related compounds
|
Benzaldehyde, Benzyl alcohol, Benzoyl chloride, Benzylamine, Benzamide, Benzonitrile | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
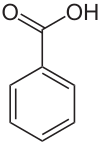
Benzoic acid (/bɛnˈzoʊ.ɪk/) is a white (or colorless) solid organic compound with the formula C6H5COOH, whose structure consists of a benzene ring (C6H6) with a carboxyl (−C(=O)OH) substituent. The benzoyl group is often abbreviated "Bz" (not to be confused with "Bn," which is used for benzyl), thus benzoic acid is also denoted as BzOH, since the benzoyl group has the formula –C6H5CO. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, which was for a long time its only source.
Benzoic acid occurs naturally in many plants[9] and serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of many secondary metabolites. Salts of benzoic acid are used as food preservatives. Benzoic acid is an important precursor for the industrial synthesis of many other organic substances. The salts and esters of benzoic acid are known as benzoates (/ˈbɛnzoʊ.eɪt/).
- ^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 745. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-00648. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "benzoic acid". chemister.ru. Retrieved 24 October 2018.
- ^ Seidell, Atherton; Linke, William F. (1952). Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds. Van Nostrand.
- ^ a b c Benzoic acid in Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (eds.); NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD) (retrieved 2014-05-23)
- ^ Harris, Daniel (2010). Quantitative Chemical Analysis (8 ed.). New York: W. H. Freeman and Company. pp. AP12. ISBN 9781429254366.
- ^ Olmstead, William N.; Bordwell, Frederick G. (1980). "Ion-pair association constants in dimethyl sulfoxide". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 45 (16): 3299–3305. doi:10.1021/jo01304a033.
- ^ a b c d Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ^ a b c Sigma-Aldrich Co., Benzoic acid. Retrieved on 2014-05-23.
- ^ "Scientists uncover last steps for benzoic acid creation in plants". Purdue Agriculture News.