| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
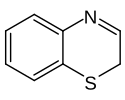
| IUPAC name
2H-1,4-benzothiazine
| |||
| Other names
1,4-benzothiazine
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
| ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H7NS | |||
| Molar mass | 149.21288 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Benzothiazine is a heterocyclic compound consisting of a benzene ring attached to the 6-membered heterocycle thiazine. The name is applied to both the 2H- and 4H-isomers of the molecule.
2,1-Benzothiazine, a type of benzothiazines was first reported in the 1960s. Subsequently, their preparation and intensive biological and physiological studies have been reported. In recent years, 2,1-benzothiazines have been of enormous interest to synthetic chemists. An enantioselective synthesis of such benzothiazines has been developed by Harmata and Hong who have formulated transformations of these compounds designed to target chiral, non-racemic building blocks as well as natural products.