| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
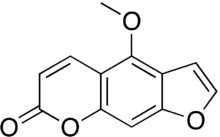
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Methoxy-7H-furo[3,2-g][1]benzopyran-7-one | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.913 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1759 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 216.192 g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| D05BA03 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Bergapten (5-methoxypsoralen) is a naturally-occurring organic chemical compound produced by numerous plant species, especially from the carrot family Apiaceae and the citrus family Rutaceae. For example, bergapten has been extracted from 24 species of the genus Heracleum in the family Apiaceae.[1][2] In the family Rutaceae, various Citrus species contain significant amounts of bergapten,[3] especially the bergamot orange, the micrantha, and certain varieties of lime and bitter orange.
Bergapten belongs to a class of chemical compounds known as the furanocoumarins. In 1834, Kalbrunner isolated 5-methoxypsoralen from bergamot essential oil,[4] hence the common name "bergapten". It was the first furanocoumarin to be isolated and identified.
- ^ Nielsen, B. E. (1970). Coumarins of Umbelliferous plants. Copenhagen: Royal Danish School of Pharmacy. Cited by Mitchell and Rook (1979).
- ^ Mitchell, John; Rook, Arthur (1979). Botanical Dermatology: Plants and Plant Products Injurious to the Skin. Vancouver: Greengrass. pp. 692–699.
- ^ Dugrand-Judek, Audray; Olry, Alexandre; Hehn, Alain; Costantino, Gilles; Ollitrault, Patrick; Froelicher, Yann; Bourgaud, Frédéric (November 2015). "The Distribution of Coumarins and Furanocoumarins in Citrus Species Closely Matches Citrus Phylogeny and Reflects the Organization of Biosynthetic Pathways". PLOS ONE. 10 (11): e0142757. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1042757D. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0142757. PMC 4641707. PMID 26558757.
- ^ Scott, B. R.; Pathak, M. A.; Mohn, G. R. (1976). "Molecular and genetic basis of furocoumarin reactions". Mutat Res. 39 (1): 29–74. doi:10.1016/0165-1110(76)90012-9. PMID 13299.