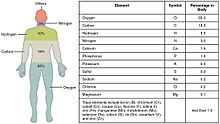
Biometals (also called biocompatible metals, bioactive metals, metallic biomaterials) are metals normally present, in small but important and measurable amounts, in biology, biochemistry, and medicine. The metals copper, zinc, iron, and manganese are examples of metals that are essential for the normal functioning of most plants and the bodies of most animals, such as the human body. A few (calcium, potassium, sodium) are present in relatively larger amounts, whereas most others are trace metals, present in smaller but important amounts (the image shows the percentages for humans). Approximately 2/3 of the existing periodic table is composed of metals with varying properties,[1] accounting for the diverse ways in which metals (usually in ionic form) have been utilized in nature and medicine.
- ^ Feig AL, Uhlenbeck OC (1999). "The role of metal ions in RNA biochemistry" (PDF). Cold Spring Harbor Monograph Series. 37: 287–320. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-03-01. Retrieved 2014-07-26.