 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Fleet, Dulcolax, Brooklax, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601027 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth or rectal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 15% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP450-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 16 Hours |
| Excretion | primarily in the feces, systemically absorbed drug is excreted in the urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.132 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
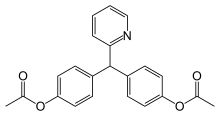
| Formula | C22H19NO4 |
| Molar mass | 361.397 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Bisacodyl (INN) is an organic compound that is used as a stimulant laxative drug. It works directly on the colon to produce a bowel movement. It is typically prescribed for relief of episodic and chronic constipation and for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction, as well as part of bowel preparation before medical examinations, such as for a colonoscopy.[2][3]
Bisacodyl is a derivative of triphenylmethane. It was first used as a laxative in 1953 because of its structural similarity to phenolphthalein.[4][5]
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6]
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ Wexner SD, Beck DE, Baron TH, Fanelli RD, Hyman N, Shen B, Wasco KE (June 2006). "A consensus document on bowel preparation before colonoscopy: prepared by a task force from the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS), the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE), and the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES)". Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 63 (7): 894–909. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2006.03.918. PMID 16733101.
- ^ Wald A (January 2016). "Constipation: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment". JAMA (Review). 315 (2): 185–91. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.16994. PMID 26757467.
- ^ Stiens SA, Luttrel W, Binard JE (November 1998). "Polyethylene glycol versus vegetable oil based bisacodyl suppositories to initiate side-lying bowel care: a clinical trial in persons with spinal cord injury". Spinal Cord. 36 (11): 777–81. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.3100702. PMID 9848486.
- ^ Evans IL (1964). "Methods and techniques: The use of Bisacodyl suppositories in preparation for sigmoidoscopy". Gut. British Medical Journal. 5: 271–3. doi:10.1136/gut.5.3.271. PMC 1552120. PMID 14178715.
- ^ World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/345533. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.