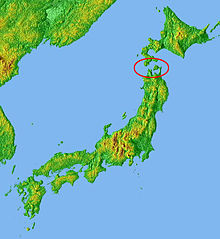
The Blakiston Line or Blakiston's Line is a faunal boundary line drawn between two of the four largest islands of Japan: Hokkaidō in the north and Honshū, south of it. It can be compared with faunal boundary lines like the Wallace Line. Certain animal species can only be found north of Blakiston's Line, while certain other species can only be found south of it.
Thomas Blakiston, who lived in Japan from 1861 to 1884 and who spent much of that time in Hakodate, Hokkaido, was the first person to notice that animals in Hokkaidō, Japan's northern island, were related to northern Asian species, whereas those on Honshū to the south were related to those from southern Asia. The Tsugaru Strait between the two islands was therefore established as a zoogeographical boundary, and became known as Blakiston's Line. This finding was first published to the Asiatic Society of Japan in a paper of 14 February 1883, named Zoological Indications of Ancient Connection of the Japan islands with the Continent.[1]
- ^ Collection Writings of Sir Hugh Cortazzi, Volume II, Sir Hugh Cortazzi, Routledge, Oxon, 2000