| Blastocyst | |
|---|---|
 Blastocyst just before implantation | |
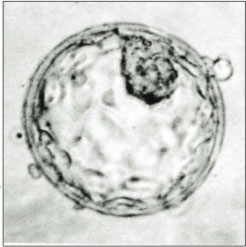 A human blastocyst, with inner cell mass at upper right | |
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 3 |
| Days | 5–9 |
| Gives rise to | Gastrula |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | blastocystis |
| MeSH | D001755 |
| TE | E2.0.1.2.0.0.12 |
| FMA | 83041 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryonic development of mammals. It possesses an inner cell mass (ICM) also known as the embryoblast which subsequently forms the embryo, and an outer layer of trophoblast cells called the trophectoderm.[1][2] This layer surrounds the inner cell mass and a fluid-filled cavity or lumen known as the blastocoel.[3] In the late blastocyst, the trophectoderm is known as the trophoblast.[2] The trophoblast gives rise to the chorion and amnion, the two fetal membranes that surround the embryo. The placenta derives from the embryonic chorion (the portion of the chorion that develops villi) and the underlying uterine tissue of the mother.[4][5] The corresponding structure in non-mammalian animals is an undifferentiated ball of cells called the blastula.
In humans, blastocyst formation begins about five days after fertilization when a fluid-filled cavity opens up in the morula, the early embryonic stage of a ball of 16 cells. The blastocyst has a diameter of about 0.1–0.2 mm and comprises 100-200 cells following 7-8 rounds of cleavage (cell division without cell growth). About seven days after fertilization,[6] the blastocyst undergoes implantation, embedding into the endometrium of the uterine wall where it will undergo further developmental processes, including gastrulation. Embedding of the blastocyst into the endometrium requires that it hatches from the zona pellucida, the egg coat that prevents adherence to the fallopian tube as the pre-embryo makes its way to the uterus.
The use of blastocysts in in vitro fertilization (IVF) involves culturing a fertilized egg for five days before transferring it into the uterus. It can be a more viable method of fertility treatment than traditional IVF. The inner cell mass of blastocysts is the source of embryonic stem cells, which are broadly applicable in stem cell therapies including cell repair, replacement and regeneration. Assisted zona hatching may also be used in IVF and other fertility treatments.
The name "blastocyst" arises from the Greek βλαστός blastós ("a sprout") and κύστις kýstis ("bladder, capsule").
- ^ "27.2C: Blastocyst Formation". Medicine LibreTexts. 24 July 2018. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ^ a b Standring, Susan (2016). Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice (Forty-first ed.). [Philadelphia]: Elsevier Limited. p. 167. ISBN 9780702052309.
- ^ Gilbert, Scott F. (2000). "Early Mammalian Development". Developmental Biology. 6th edition. Retrieved 13 May 2022.
- ^ "trophoblast | embryology". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2021-11-01.
- ^ Solomon, Eldra (2018). Biology 11th Edition. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1337392938.
- ^ VanPutte C (2020). Seeley's Anatomy & Physiology. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 1092. ISBN 978-1-260-56596-6. OCLC 1099344977.