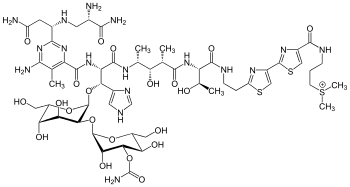
 Bleomycin A2 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Blenoxane |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682125 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intrapleural[2] |
| Drug class | Glycopeptide antibiotic |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 100% and 70% following intramuscular and subcutaneous administrations, respectively, and 45% following both intraperitoneal and intrapleural administrations[2] |
| Elimination half-life | two hours[2] |
| Excretion | Kidney (60–70%)[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C55H84N17O21S3 |
| Molar mass | 1415.56 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Bleomycin is a medication used to treat cancer.[6] This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, and cervical cancer among others.[6] Typically used with other cancer medications,[6] it can be given intravenously, by injection into a muscle or under the skin.[6] It may also be administered inside the chest to help prevent the recurrence of a pleural effusion due to cancer; however talc is better for this.[6][7]
Common side effects include fever, weight loss, vomiting, and rash.[6] A severe type of anaphylaxis may occur.[6] It may also cause inflammation of the lungs that can result in lung scarring.[6] Chest X-rays every couple of weeks are recommended to check for this.[6] Bleomycin may cause harm to the baby if used during pregnancy.[6] It is believed to primarily work by preventing the synthesis of DNA.[6]
Bleomycin was discovered in 1962.[8][9] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[10] It is available as a generic medication.[6] It is made by the bacterium Streptomyces verticillus.[6]
- ^ "Bleomycin Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 9 August 2019. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ a b c d "Bleomycin- bleomycin sulfate injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution". DailyMed. 31 December 2019. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "Bleo-Kyowa Powder for solution for injection - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 31 August 2018. Archived from the original on 16 February 2020. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- ^ "Bleomycin". European Medicines Agency (EMA).
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Bleomycin Sulfate". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 8 September 2015. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ^ Dipper A, Jones HE, Bhatnagar R, Preston NJ, Maskell N, Clive AO (April 2020). "Interventions for the management of malignant pleural effusions: a network meta-analysis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020 (4): CD010529. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010529.pub3. PMC 7173736. PMID 32315458.
- ^ Sneader W (2005). Drug discovery : a history (Rev. and updated ed.). Chichester: Wiley. p. 312. ISBN 9780471899792. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016.
- ^ Phillips GO (2018). Innovation and Technology Transfer in Japan and Europe: Industry-Academic Interactions. Routledge. p. PT155. ISBN 9780429774546.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.