| Logical connectives | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related concepts | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
In mathematics, a Boolean function is a function whose arguments and result assume values from a two-element set (usually {true, false}, {0,1} or {-1,1}).[1][2] Alternative names are switching function, used especially in older computer science literature,[3][4] and truth function (or logical function), used in logic. Boolean functions are the subject of Boolean algebra and switching theory.[5]
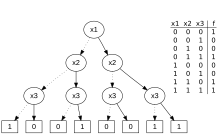
A Boolean function takes the form , where is known as the Boolean domain and is a non-negative integer called the arity of the function. In the case where , the function is a constant element of . A Boolean function with multiple outputs, with is a vectorial or vector-valued Boolean function (an S-box in symmetric cryptography).[6]
There are different Boolean functions with arguments; equal to the number of different truth tables with entries.
Every -ary Boolean function can be expressed as a propositional formula in variables , and two propositional formulas are logically equivalent if and only if they express the same Boolean function.
- ^ "Boolean function - Encyclopedia of Mathematics". encyclopediaofmath.org. Retrieved 2021-05-03.
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Boolean Function". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2021-05-03.
- ^ "switching function". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 2021-05-03.
- ^ Davies, D. W. (December 1957). "Switching Functions of Three Variables". IRE Transactions on Electronic Computers. EC-6 (4): 265–275. doi:10.1109/TEC.1957.5222038. ISSN 0367-9950.
- ^ McCluskey, Edward J. (2003-01-01), "Switching theory", Encyclopedia of Computer Science, GBR: John Wiley and Sons Ltd., pp. 1727–1731, ISBN 978-0-470-86412-8, retrieved 2021-05-03
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:2was invoked but never defined (see the help page).










































