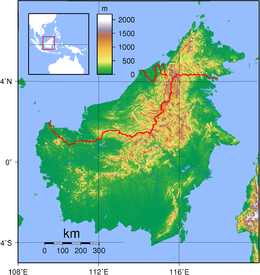
 Topography of Borneo | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Southeast Asia |
| Coordinates | 0°N 114°E / 0°N 114°E |
| Archipelago | Indonesian Archipelago
Greater Sunda Islands |
| Area | 748,168 km2 (288,869 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 3rd |
| Highest elevation | 13,435 ft (4095 m) |
| Highest point | Mount Kinabalu |
| Administration | |
| Districts | Belait Brunei and Muara Temburong Tutong |
| Largest settlement | Bandar Seri Begawan (pop. ~150,000) |
| Provinces | |
| Largest settlement | Samarinda (pop. 842,691) |
| States and FT | |
| Largest settlement | Kota Kinabalu (pop. 500,421) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 21,258,000 (2023 Censuses)[1][2][3] (2023) |
| Pop. density | 30.8/km2 (79.8/sq mi) |
Borneo (/ˈbɔːrnioʊ/; also known as Kalimantan in the Indonesian language) is the third-largest island in the world, with an area of 748,168 km2 (288,869 sq mi). Situated at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, it is one of the Greater Sunda Islands, located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and east of Sumatra.
The island is politically divided among three countries: Malaysia and Brunei in the north, and Indonesia to the south.[4] Approximately 73% of the island is Indonesian territory. In the north, the East Malaysian states of Sabah and Sarawak make up about 26% of the island. The population in Borneo is 23,053,723 (2020 national censuses).[1][2][3]
Additionally, the Malaysian federal territory of Labuan is situated on a small island just off the coast of Borneo. The sovereign state of Brunei, located on the north coast, comprises about 1% of Borneo's land area. A little more than half of the island is in the Northern Hemisphere, including Brunei and the Malaysian portion, while the Indonesian portion spans the Northern and Southern hemispheres.
- ^ a b Sugianto, Danang. "Sensus Penduduk 2020 Selesai, Begini Sebaran Masyarakat RI Terbaru". finance.detik.com. Retrieved 27 September 2022.
- ^ a b Malaysia: Federal States, Territories, Districts, Major Cities, Urban Aras & Conurbations - Statistics & Maps on City Population. Citypopulation.de (2013-05-20). Retrieved on 2013-07-12.
- ^ a b "W.P. Labuan Sepintas Lalu". statistics.gov.my. Archived from the original on 13 November 2014. Retrieved 19 September 2014.
- ^ Donna Marchetti (2 August 1998). "Borneo's Wild Side". The New York Times. Retrieved 20 June 2017.