| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Boron trichloride
| |||
| Other names
Boron(III) chloride
Trichloroborane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.586 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| BCl3 | |||
| Molar mass | 117.17 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas, fumes in air | ||
| Density | 1.326 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −107.3 °C (−161.1 °F; 165.8 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 12.6 °C (54.7 °F; 285.8 K)[1] | ||
| hydrolysis | |||
| Solubility | soluble in CCl4, ethanol | ||
| -59.9·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.00139 | ||
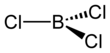
| Structure | |||
| Trigonal planar (D3h) | |||
| zero | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
107 J/mol K | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
206 J/mol K | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-427 kJ/mol | ||
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
-387.2 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards[2] | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
May be fatal if swallowed or if inhaled Causes serious burns to eyes, skin, mouth, lungs, etc. Contact with water gives HCl | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H300, H314, H330[note 1] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | Non-flammable | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
Boron trifluoride Boron tribromide Boron triiodide | ||
Other cations
|
Aluminium trichloride Gallium trichloride | ||
Related compounds
|
Boron trioxide Carbon tetrachloride | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Boron trichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula BCl3. This colorless gas is a reagent in organic synthesis. It is highly reactive towards water.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
EROSwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Index no. 005-002-00-5 of Annex VI, Part 3, to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. OJEU L353, 31.12.2008, pp 1–1355 at p 341.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).