 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Velcade, others |
| Other names | PS-341 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607007 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Subcutaneous, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 83% |
| Metabolism | Liver, CYP extensively involved |
| Elimination half-life | 9 to 15 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.125.601 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
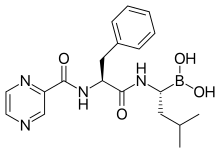
| Formula | C19H25BN4O4 |
| Molar mass | 384.24 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Bortezomib, sold under the brand name Velcade among others, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma.[4] This includes multiple myeloma in those who have and have not previously received treatment.[3] It is generally used together with other medications.[3] It is given by injection.[4]
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, tiredness, low platelets, fever, numbness, low white blood cells, shortness of breath, rash and abdominal pain.[4] Other severe side effects include low blood pressure, tumour lysis syndrome, heart failure, and reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome.[4][3] It is in the class of medications known as proteasome inhibitor.[4] It works by inhibiting proteasomes, cellular complexes that break down proteins.[3]
Bortezomib was approved for medical use in the United States in 2003 and in the European Union in 2004.[4][3] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[5] It is available as a generic medication.[6]
- ^ "Bortezomib Baxter (Baxter Healthcare Pty Ltd)". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 2 May 2024. Retrieved 5 October 2024.
- ^ "Boruzu- bortezomib injection". DailyMed. 27 September 2024. Retrieved 11 November 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f "Velcade EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f "Bortezomib Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ "2022 First Generic Drug Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 3 March 2023. Archived from the original on 30 June 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.