| Brachialis | |
|---|---|
 Deep muscles of the chest and front of the arm, with the boundaries of the axilla. (Brachialis visible at bottom right.) | |
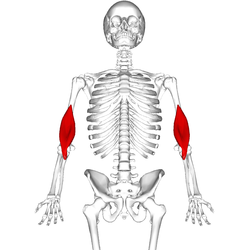 Position of brachialis (shown in red). | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Anterior surface of the humerus, particularly the distal half of this bone |
| Insertion | Coronoid process and the tuberosity of the ulna |
| Artery | Radial recurrent artery, brachial artery |
| Nerve | Musculocutaneous nerve (C5-C7) and radial nerve (C5, C6) |
| Actions | Flexion at elbow joint |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus brachialis |
| TA98 | A04.6.02.018 |
| TA2 | 2469 |
| FMA | 37667 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The brachialis (brachialis anticus) is a muscle in the upper arm that flexes the elbow. It lies beneath the biceps brachii, and makes up part of the floor of the region known as the cubital fossa (elbow pit). It originates from the anterior aspect of the distal humerus;[1] it inserts onto the tuberosity of the ulna. It is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve,[2] and commonly also receives additional innervation from the radial nerve.[3] The brachialis is the prime mover of elbow flexion generating about 50% more power than the biceps.[dubious – discuss][1]
- ^ a b Saladin, Kenneth S, Stephen J. Sullivan, and Christina A. Gan. Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. 2015. Print.
- ^ Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. p. 662,672. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- ^ "Brachialis Muscle." Kenhub. Kenhub, Aug. 2001