| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Bromine azide
| |||
| Other names
Bromo azide, Azidobromide
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
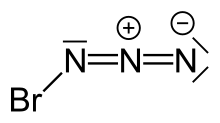
| BrN3 | |||
| Molar mass | 121.924 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Red liquid | ||
| Density | N/A | ||
| Melting point | −45 °C (−49 °F; 228 K) | ||
| Boiling point | Explodes | ||
| Structure[1] | |||
| tetragonal | |||
| I4cd | |||
Formula units (Z)
|
16 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
This is a poison that can spontaneously explode.[2] It explodes on contact with arsenic, sodium, silver foil, or phosphorus. It has a hazard class of 1.1A. | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Hydrazoic acid Fluorine azide Chlorine azide Iodine azide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Bromine azide is an explosive inorganic compound with the formula BrN3. It has been described as a crystal or a red liquid at room temperature.[citation needed] It is extremely sensitive to small variations in temperature and pressure, with explosions occurring at Δp ≥ 0.05 Torr and also upon crystallization, thus extreme caution must be observed when working with this chemical.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
solidwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Patnaik, Pradyot (2007). A Comprehensive Guide to the Hazardous Properties of Chemical Substances. 615: Wiley-Interscience. p. 615. ISBN 978-0-471-71458-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link)

