| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Bromine pentafluoride
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.234 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1745 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| BrF5 | |||
| Molar mass | 174.894 g.mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Pale yellow liquid | ||
| Density | 2.466 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −61.30 °C (−78.34 °F; 211.85 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 40.25 °C (104.45 °F; 313.40 K) | ||
| Reacts with water | |||
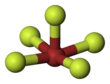
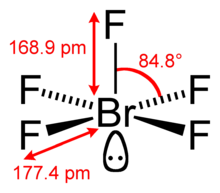
| Structure | |||
| Square pyramidal | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Powerful oxidizer, corrosive, highly toxic, reacts violently with water to release HF[1] | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H271, H300+H310+H330, H314, H372 | |||
| P210, P220, P221, P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P283, P284, P301+P310, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P306+P360, P307+P311, P309+P311, P310, P314, P320, P321, P331, P363, P370+P378, P371+P380+P375, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | Non-flammable | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
none[1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.1 ppm (0.7 mg/m3)[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[1] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS[dead link] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
Bromine monochloride | ||
Other cations
|
Chlorine pentafluoride Iodine pentafluoride | ||
Related compounds
|
Bromine monofluoride Bromine trifluoride | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Bromine pentafluoride (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Bromine pentafluoride, BrF5, is an interhalogen compound and a fluoride of bromine. It is a strong fluorinating agent.
BrF5 finds use in oxygen isotope analysis. Laser ablation of solid silicates in the presence of BrF5 releases O2 for subsequent analysis.[2] It has also been tested as an oxidizer in liquid rocket propellants and is used as a fluorinating agent in the processing of uranium.
- ^ a b c d NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0065". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Clayton, R.; Mayeda, T. K. (1963). "The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxides and silicates for isotopic analysis". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 27 (1): 43–48. Bibcode:1963GeCoA..27...43C. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(63)90071-1.