 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Bufotenine; 5-Hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine; 5-HO-DMT; 5-OH-DMT; N,N-Dimethyl-5-hydroxytryptamine; N,N-Dimethylserotonin; Dimethylserotonin; Dimethyl-5-HT; Cebilcin; Mappine |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.971 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
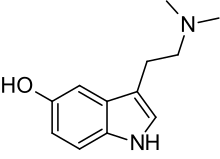
| Formula | C12H16N2O |
| Molar mass | 204.273 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 146 to 147 °C (295 to 297 °F) |
| Boiling point | 320 °C (608 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Bufotenin, also known as dimethylserotonin or as 5-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-HO-DMT), is a tryptamine derivative, more specifically, a dimethyltryptamine (DMT) analogue, related to the neurotransmitter serotonin. It is an alkaloid found in some species of mushrooms, plants and toads, especially the skin. It is also found naturally in the human body in small amounts.[1][2][3]
The name bufotenin originates from the toad genus Bufo, which includes several species of psychoactive toads, most notably Incilius alvarius, that secrete bufotoxins from their parotoid glands.[4] Bufotenin is similar in chemical structure to the psychedelics psilocin (4-HO-DMT), 5-MeO-DMT and DMT, chemicals which also occur in some of the same fungus, plant and animal species as bufotenin.
- ^ Barker SA, McIlhenny EH, Strassman R (2012). "A critical review of reports of endogenous psychedelic N, N-dimethyltryptamines in humans: 1955-2010". Drug Test Anal. 4 (7–8): 617–635. doi:10.1002/dta.422. PMID 22371425.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
NeumannDheinKirchhefer2024was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Kärkkäinen J, Forsström T, Tornaeus J, Wähälä K, Kiuru P, Honkanen A, Stenman UH, Turpeinen U, Hesso A (2005). "Potentially hallucinogenic 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor ligands bufotenine and dimethyltryptamine in blood and tissues". Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 65 (3): 189–199. doi:10.1080/00365510510013604. PMID 16095048.
- ^ Bufo Alvarius. AmphibiaWeb. Accessed on May 6, 2007.