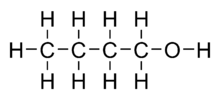
Butanol may be used as a fuel in an internal combustion engine. It is more similar to gasoline than it is to ethanol. A C4-hydrocarbon, butanol is a drop-in fuel and thus works in vehicles designed for use with gasoline without modification.[1] Both n-butanol and isobutanol have been studied as possible fuels. Both can be produced from biomass (as "biobutanol"[2][3][4] ) as well as from fossil fuels (as "petrobutanol"[5]). The chemical properties depend on the isomer (n-butanol or isobutanol), not on the production method.
- ^ "ButylFuel, LLC". Retrieved 2008-01-29.
- ^ Sampa Maiti; et al. (December 10, 2015). "Quest for sustainable bio‐production and recovery of butanol as a promising solution to fossil fuel". Energy Research. 40 (4): 411–438. doi:10.1002/er.3458. S2CID 101240621.
- ^ Alternative Fuels and Advanced Vehicles Data Center: Biobutanol
- ^ "Cobalt Biofuels | Biobutanol and Beyond". Archived from the original on 2008-10-25. Retrieved 2008-10-27.
- ^ Atsumi, Shota; Hanai, Taizo; Liao, James C. (2008), "Non-fermentative pathways for synthesis of branched-chain higher alcohols as biofuels", Nature, 451 (7174): 86–89, Bibcode:2008Natur.451...86A, doi:10.1038/nature06450, PMID 18172501, S2CID 4413113